Thermal Reduction of Cu2+ in presence of Ag+ in Clinoptilolite: Structural Study by EXAFS and HR-XRD
Abstract
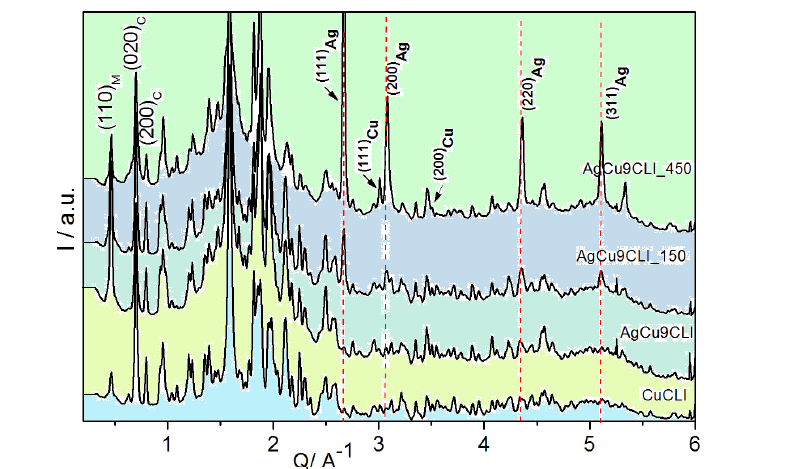
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and high resolution X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiments were carried out on Cu2+-Ag+ bimetallic system exchanged and then thermally reduced in natural clinoptilolite (CLI) from Tasajeras deposit (Cuba). The EXAFS signals of the bimetallic systems showed changes in the Cu2+ coordination as a result of their reduction at 150oC, which doesn't happen to CuCLI monometallic one. The presence of silver facilitates the reduction of Cu2+ in bimetallic systems forming only clusters. At higher reduction temperature (450oC) all mono- and bi-metallic samples exhibit mainly metallic particles of Cu and Ag with higher aggregation. These results are confirmed by XRD studies. Aggregation of reduced copper species is restricted in the presence of silver.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








