Diffusion of Hydrogen in Nanoporous Solids with Strongly Localized Adsorption Sites
Abstract
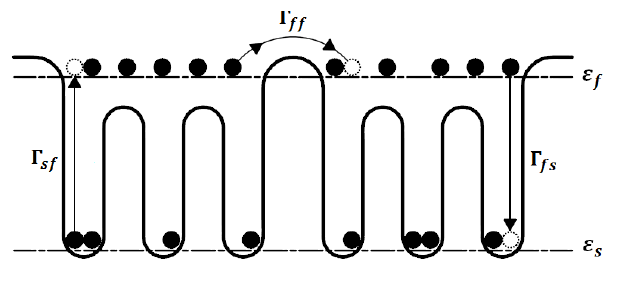
Hydrogen diffusion in a nanoporous solid where molecules can be adsorbed in both localized and non localized states is considered. A modified diffusion equation is derived, which takes into account the time delay due to transitions between states inside the same pore. Analytical solutions are obtained. The time dependence of the fraction of adsorbed molecules is studied as a function of the relative population of localized and non localized states. The effective transport diffusion coefficient decreases and shows a maximum at increasing values of loadingas the fraction of localized states grows. This study is relevant to evaluate the effect of larger adsorption enthalpies on adsorption -desorption kinetics in hydrogen storage materials.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








