Light Transport in Biological Tissues Using GPU
Abstract
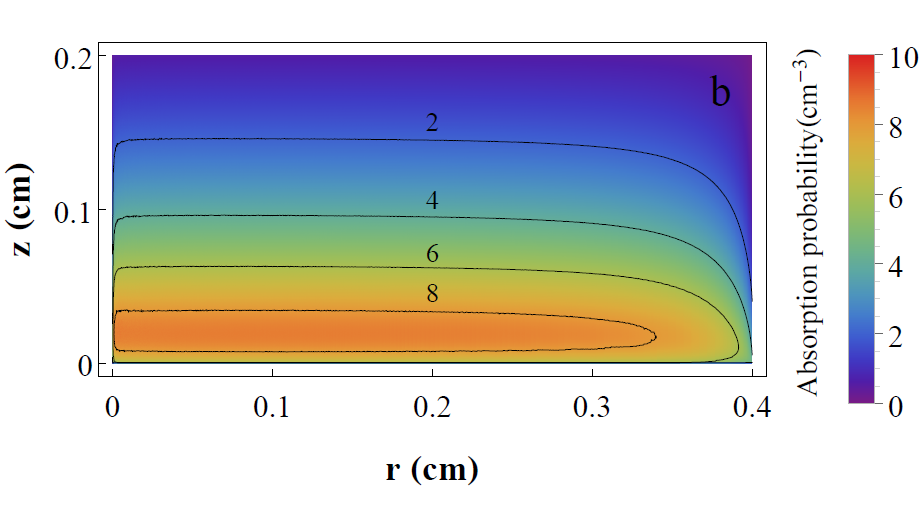
The exact solution of the propagation of light in turbid media is possible only in very simple problems. In almost all practical cases numerical methods are mandatory. In this paper we calculate the absorbance of light in tumoral tissue using Monte Carlo (MC) simulation in order to optimize the execution time of several parallel algorithms for Graphic Processing Units (GPU) and a serial code running on the Central Processing Unit (CPU) for 106 to 1010 photon packets. The plots of absorbance versus time and tissue depth are presented, showing that the precision of the methods depend on the number of photons and it is algorithm independent. The implementation of MC algorithms using GPU have shown that simulations may be 300 times faster than on a CPU providing an effective time framework to study complex systems.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








