Laser Activation to Growth ZnO Nanostructures
Abstract
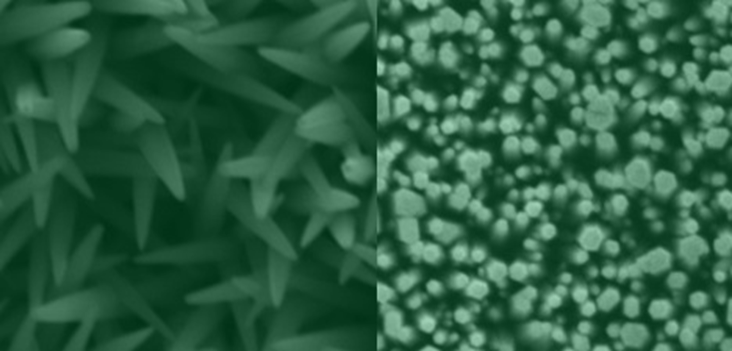
ZnO is a semiconductor material that has received an increased interest because of its excellent optical, electrical and morphological characteristics, in addition to its low cost and low toxicity. ZnO nanostructures such as nanorods have been incorporated into third generation solar cells in order to increase the surface/volume ratio. The CBD (Chemical Bath Deposition) is one of the most used techniques for obtaining nanorods because it is a low cost technique very simple to implement. One of the fundamental steps to achieve homogeneous growth of nanorods on the substrate surface is the so-called activation or sedimentation where very small crystals are formed which act as nucleation points. In this work we will approach the activation method through pulsed laser in comparison with the traditional thermal treatment.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








