Intercalation of Ciprofloxacin in Smectite: First Principles and molecular dynamics calculations
Abstract
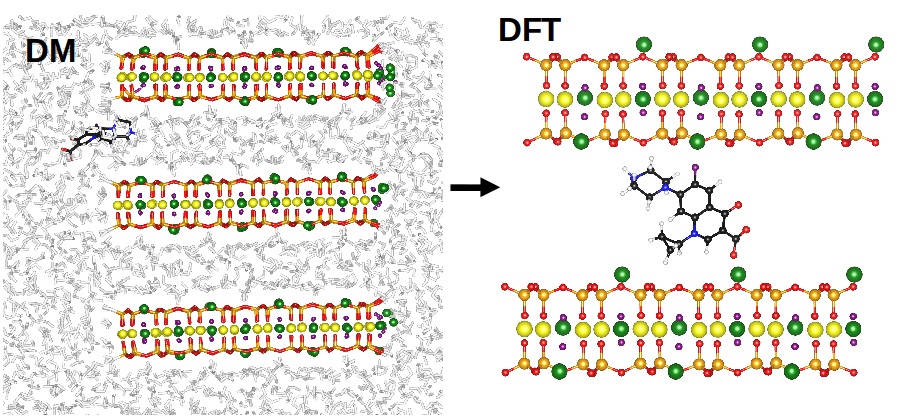
Two simulation methods, DFT and Molecular Dynamics (DM), have been used to explore the molecular details of the incorporation of ciprofloxacin (cipro) into a clay model. The electrostatic interactions between the compensating cations of the material and the groups with negative charge density of the drug, besides hydrogen bond interactions, are responsible for the stabilization of the cipro in the clay model. The DM results show a rapid migration of some Li+ cations near the edges, suggesting a charge reorganization process. It is possible to observe at least two attempts of intercalation of the drug. Only when the drug-clay composite material is in contact with water, it is possible to observe the diffusion of a Li+ cation and the early stages of the swelling process. The results indicate that the cipro molecule in solution plays an important role favoring the stacking process in this clay.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








