Abstract
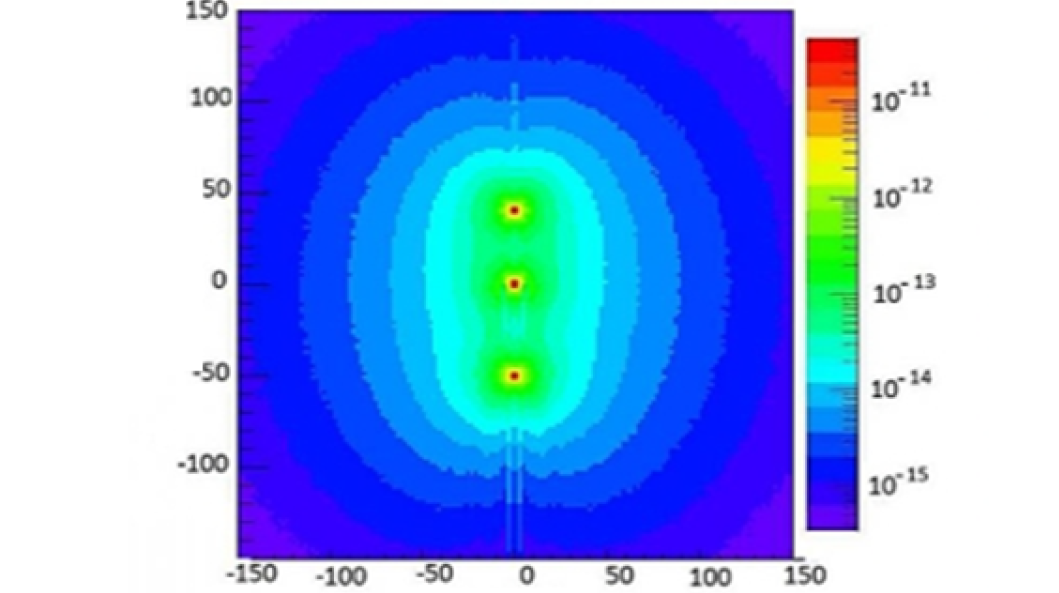
The study aims to evaluate the absorbed dose (Dabs) in high-dose-rate brachytherapy treatments with a source of 192Ir, considering the heterogeneities of the tissues, types of applicators and patient dimensions. To this end, isodose calculations by Monte Carlo (MC) simulation and a test of accuracy of the dose delivered to a simulator object were performed, comparing the Dabs planned in the treatment planning system (TPS) with the dose recorded by the optically stimulated luminescence dosimeter. It was found that the TPS adequately calculates the distribution of Dabs when the medium is water; however, it is necessary to include libraries that consider heterogeneities in order to perform a more precise calculation of the distribution of Dabs in patients. It is concluded that performing a CM simulation is a good option to test whether the TPS calculates the Dabs in the presence of heterogeneities.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista Cubana de Física