Stability of a Natural Palygorskite after a Cycle of Adsorption-Desorption of an Emerging Pollutant
Abstract
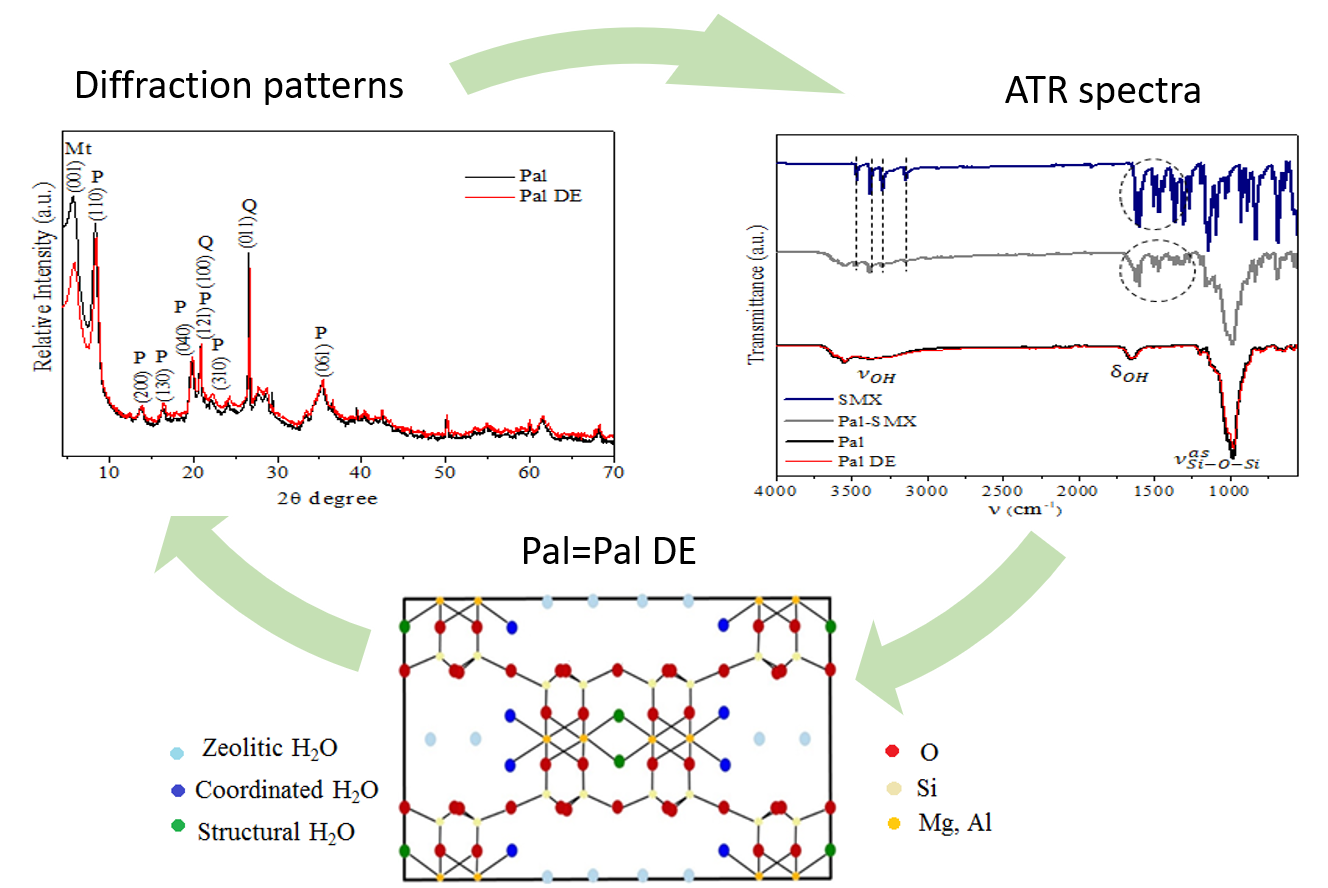
In the present study, we evaluate the structural stability of a natural Cuban clay –an adsorbent of organic pollutants– after an adsorption/desorption process. The clay under study was palygorskite (Pal), and sulfamethoxazole (SMX) was the emerging contaminant. The materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), attenuated total reflection (ATR) infrared spectroscopy and zeta potential (ZP) before and after the SMX adsorption/desorption processes. Based on the material integrity, the potentiality of Pal as pollutant adsorbent and its possible reuse in adsorption/desorption cycles was demonstrated.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








