Effect of the Zr/Ti Ratio on the Properties of the PZT Ceramic Modified with 0.05 mol of Strontium
Abstract
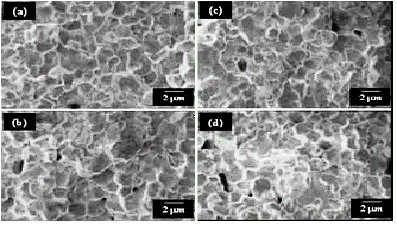
Ceramics corresponding to the lead titanate zirconate (PZT) ceramic system modified with strontium in different regions of phase diagram (Zr/Ti = 20/80, 40/60, 53/47, 60/40), were sinterized at 1290 ºC for 70 minutes, the optimal sintering regimen according to previous studies. Tetragonal and rombohedral phases were obtained (mixed rombohedral and tetragonal were obtained for Zr/Ti = 53/47). As the Zr/Ti ratio increases, tetragonality and Curie temperature decreases, while the grain size did not show a noticeable variation. Our samples showed normal ferroelectric/paraelectric transitions and a Curie-Weiss behaviour above transition temperature.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








